How ERP Works in an Organization
Dec 27, 2024

Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become essential tools for businesses seeking efficiency and growth. By integrating processes and automating workflows, ERP transforms the way organizations operate. This article explores how ERP works within a company, driving better data management, productivity, and decision-making.
ERP, or Enterprise Resource Planning, is software that unifies core business processes into a single system. Instead of using separate tools for finance, inventory, HR, or sales, ERP consolidates everything under one platform. This integration promotes efficiency, reduces errors, and provides companies with a clear view of operations.
Think of ERP as the backbone of a business—it strengthens every department, ensuring they work together seamlessly. Whether you’re tracking inventory, managing payroll, or generating invoices, ERP keeps everything aligned.
ERP systems consist of modules, each tailored to manage specific functions. The most common modules include:
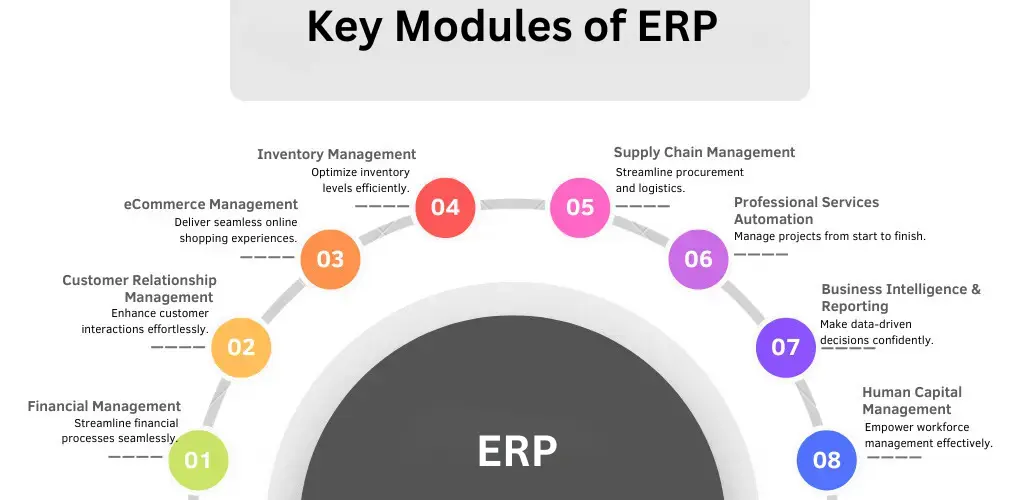
Companies can select modules based on their needs, making ERP highly adaptable.
One of ERP’s key strengths is integration. It connects departments to ensure vital data flows freely. For example, when a sales rep closes a deal, the system automatically updates inventory, billing, and order history. This centralized approach reduces redundant tasks and boosts collaboration across teams.
Here’s how data moves within an ERP system:
This workflow ensures communication between departments while speeding up operations.
Because ERP centralizes information, errors like duplicate records or outdated data are eliminated. Instead of departments working with conflicting numbers, everyone relies on a single source of truth. This consistency improves accuracy across the organization.
ERP systems provide real-time insights into business operations. Managers can track performance metrics, inventory levels, or financials without waiting for manual updates. This immediate access helps businesses stay agile in competitive markets.
Having up-to-date information is a game-changer for decision-making. For instance, leaders can use real-time data to adjust budgets, predict sales trends, or plan inventory purchases. Quick access to insights helps avoid costly mistakes.
Imagine a manager notices a build-up of outdated inventory. Using ERP, the manager identifies slow-moving products and halts future orders, saving money and warehouse space.
In traditional setups, teams often work in isolation. ERP breaks down these barriers by sharing information across departments. For example, when a purchase order is submitted through ERP, both Sales and Accounts Payable have instant visibility. This alignment prevents communication gaps and redundancies.
When Sales closes a large customer order, the ERP system notifies Finance to generate an invoice. At the same time, the warehouse receives an automatic pick list. These synchronized actions reduce delays and improve accuracy.
Customer satisfaction also improves with ERP. The system ensures that customers receive updates on their orders and faster responses to their questions. For example, tracking an order’s delivery status becomes a simple, automated task.
ERP systems take over repetitive tasks like data entry, invoice generation, and order processing. This allows employees to focus on strategic roles rather than mundane work, increasing their productivity.
Automation reduces human errors. For example, when generating financial reports, ERP automatically ensures that calculations are accurate. This improves compliance and reduces costly mistakes.
By automating processes, ERP dramatically reduces the time needed for tasks. What once required hours—like reconciling accounts or managing inventory—can now be completed in minutes.
ERP systems centralize all business data, making it more manageable. Managers can control access, ensuring only authorized employees handle sensitive information.
Dashboards and key performance indicators (KPIs) allow managers to monitor operations at a glance. Whether it’s revenue, inventory, or workforce performance, ERP provides a clear overview.
A CEO using ERP can quickly see real-time updates on revenue, inventory levels, and staff productivity. This visibility supports strategic planning and long-term growth.
ERP evolves with your business. Whether you’re entering new markets or expanding your product line, the system can handle growing demands without disrupting operations.
Modern ERP systems allow businesses to customize settings. Companies can adjust workflows or add modules to meet specific needs.
Expanding internationally? ERP ensures consistent operations across multiple locations, from currency conversions to tax compliance. This consistency makes global growth smoother and more manageable.
ERP simplifies reporting by consolidating data across departments. Whether it’s financial summaries or performance metrics, reports are instantly generated and highly accurate.
With built-in analytics, ERP predicts trends and offers actionable insights. Businesses can use this data to optimize operations or forecast market demands.
A finance team spotting a seasonal dip in revenue might use ERP analytics to adjust upcoming budgets in advance.
Introducing ERP can come with hurdles, such as data migration issues, employee resistance, or high upfront costs. Careful planning mitigates these risks.
To ensure employees embrace ERP, offer regular training and support. Show them how the system simplifies their work to increase buy-in.
By automating tasks and streamlining workflows, ERP allows employees to dedicate time to strategic work, boosting productivity.
ERP enhances service by updating customers about orders, resolving issues quickly, and improving order accuracy.
With ERP systems analyzing data continuously, businesses discover areas for improvement. This drives innovation and keeps companies competitive.
ERP connects, automates, and optimizes processes within an organization, transforming how businesses operate. From real-time data access to breaking down departmental silos, ERP boosts efficiency and collaboration while reducing errors and saving time. Its scalability and adaptability ensure it grows alongside your business. For organizations looking to stay competitive, adopting ERP is no longer a choice—it’s a necessity. Evaluate your current systems today and explore ERP to unlock long-term success.